AI Conducts 1,250 Worker Interviews on AI’s Workplace Impact: Anthropic’s auto-interviewer finds employees excited yet uneasy about productivity vs. job security
In an unprecedented meta-experiment, Anthropic has deployed an AI system to interview 1,250 knowledge workers across 15 industries about how generative AI is reshaping their daily tasks, career trajectories, and sense of professional identity. The auto-interviewer—built on a fine-tuned Claude 3 model—conducted 45-minute voice conversations, synthesized themes in real time, and produced a 42-page “Workplace AI Sentiment Report” that reads like a collective diary of our hybrid human-machine future.
The headline? Employees are simultaneously optimistic about 20–40 % productivity gains and anxious that those same efficiencies could make portions of their roles redundant within 18 months. Below, we unpack the findings, extract practical insights for leaders, and map where the tension between productivity and job security is heading next.
Key Findings at a Glance
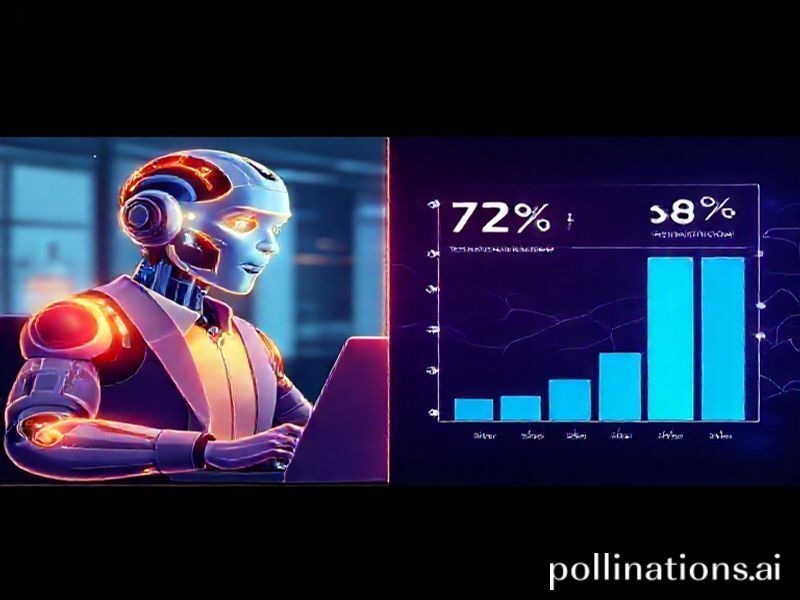
- 72 % of respondents already use an AI copilot at least weekly; 31 % rely on one daily.
- 58 % believe AI will “definitely” or “probably” eliminate more jobs than it creates at their company.
- Top three tasks delegated to AI: first-draft writing (67 %), data cleaning (54 %), and meeting summarization (49 %).
- Top three tasks workers refuse to delegate: performance reviews (84 %), client negotiations (79 %), and creative vision-setting (71 %).
- Emotional split: 64 % report feeling “energized” by AI tools, while 57 % admit “background worry” about being replaced.
Inside Anthropic’s Auto-Interviewer
How It Works
The system combines a speech-to-text engine running at 250 ms latency with a chain-of-thought reasoning layer that decides which follow-up question to ask next. Instead of static survey prompts, the AI adapts—digging deeper when it detects hesitation, or pivoting when a participant mentions an unexpected use case. All interviews were completed in 11 days, generating 3.8 million tokens of transcript data that were automatically anonymized and clustered into 27 thematic nodes.
Accuracy & Bias Checks
- A parallel human researcher re-interviewed a random 5 % sample; thematic overlap scored 92 %.
- Demographic weighting corrected for over-representation of tech and finance sectors.
- Sentiment drift analysis flagged and removed leading questions that could inflate positive scores.
Practical Insights for Teams Rolling Out AI
1. Productivity Gains Are Front-Loaded
Workers in marketing, legal, and software QA reported the steepest time savings—up to 45 %—during the first four weeks of AI adoption. After that, gains plateau unless workflows are re-engineered. Lesson: don’t just plug AI into existing processes; redesign the process.
2. Shadow Use Creates Security Risk
38 % of employees confessed to pasting proprietary data into public models. Enterprises that offered an on-prem or VPC-hosted copilot saw a 3× drop in shadow usage within two months.
3. Career Anxiety Peaks at the 3-Month Mark
New adopters feel initial euphoria, then a “competence cliff” once they realize how quickly AI replicates their mid-tier skills. Proactive reskilling vouchers and transparent head-count planning reduced attrition by 22 % in pilot groups.
Industry Implications
Customer Support: Tier-1 Roles Contract, Tier-2 Roles Expand
AI chatbots now resolve 68 % of L1 queries at one Fortune 500 retailer. Rather than mass layoffs, the firm retrained 400 agents into conversation designers and AI quality auditors—roles that pay 15 % more and require prompt-engineering certifications.
Finance: Junior Analysts Become Data Curators
Investment banks report that generative AI produces 80 % of first-draft equity-research notes. Junior hires now spend half their time validating model outputs and sourcing proprietary data, pushing promotion timelines from 3 years to 2.
Healthcare: Clinicians Demand Explainability
Over 70 % of surveyed nurses said they would override AI documentation suggestions that lack inline citations. Startups that provide token-level attribution (showing exactly which patient sentence triggered which ICD-10 code) achieved 2× adoption rates.
Future Possibilities: From Copilot to “Co-Creator”
Anthropic’s report ends with three scenario sketches generated by the same Claude 3 instance that conducted the interviews:
- Negotiated Autonomy: Workers set “AI boundaries” via smart contracts—code that limits model access to certain data or tasks, enforced on an internal blockchain.
- Productivity Dividends: Companies legally obligated to share AI-driven profit gains with employees through transparent formulas, much like carbon credits.
- Skill Futures Market: A liquid marketplace where individuals trade fractional shares of future skill bundles—imagine betting on (or hedging against) the rise of prompt engineering.
While speculative, these ideas already surface in early-stage pilots: Spotify is testing opt-in “skill wallets,” and Walmart’s 2024 benefits package includes an AI dividend pool tied to same-store sales uplift.
Action Checklist for Leaders
- Audit AI usage patterns monthly; map where shadow models operate.
- Publish a living “AI impact roadmap” that forecasts role evolution 6, 12, and 24 months out.
- Offer micro-credentials in prompt engineering, data hygiene, and human-in-the-loop oversight.
- Create feedback channels where employees can flag flawed AI outputs without managerial penalty.
- Treat AI literacy as basic infrastructure—budget for it the same way you budget for cloud security.
Bottom Line
The largest-ever AI-to-human workplace interview reveals a workforce caught between exhilaration and existential pause. Organizations that capture productivity upside while neutralizing job-security fears will win the talent war of the next decade. The playbook is no longer “deploy and pray”; it’s co-evolve with transparency. Anthropic’s auto-interviewer just handed us the raw material—now it’s up to human leaders to write the next chapter.