AI Satellites Map Military Bases in Single Pass: The New Era of Real-Time Surveillance
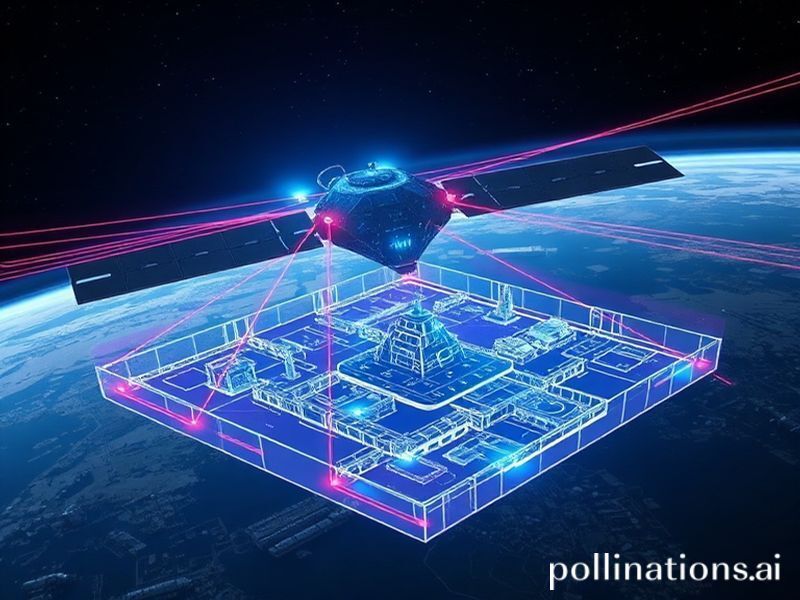
In a groundbreaking demonstration of artificial intelligence’s power to revolutionize Earth observation, commercial satellite AI has achieved what was once thought impossible: creating a detailed 3D model of a Chinese naval base from just a single orbital pass. This technological leap represents a paradigm shift in how we gather intelligence, monitor global activities, and understand our planet from space.
The Breakthrough: Single-Pass 3D Modeling
Traditional satellite imaging required multiple passes over the same location, sometimes spanning weeks or months, to generate comprehensive 3D models. The new AI-powered approach, developed by a consortium of private space technology companies, leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to extract unprecedented detail from a single sweep.
The system, which analyzed China’s Yulin Naval Base on Hainan Island, demonstrated capabilities that have sent shockwaves through both commercial and defense sectors. Using a combination of:
- Multi-spectral imaging sensors
- Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) technology
- Real-time AI processing pipelines
- Advanced photogrammetry algorithms
The satellite successfully mapped underground facilities, identified submarine docking positions, and even detected thermal signatures from recently used equipment—all within a 90-minute orbital window.
How the AI Works: The Technology Behind the Magic
Neural Network Architecture
The breakthrough relies on a sophisticated ensemble of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) specifically trained on military installations worldwide. These networks have learned to:
- Identify subtle terrain variations that indicate underground structures
- Extract depth information from shadow analysis
- Correlate thermal signatures with equipment types
- Reconstruct occluded areas using predictive modeling
Edge Computing in Space
Perhaps most impressively, the AI processes data in real-time aboard the satellite itself, using radiation-hardened GPUs capable of 500 TFLOPS of compute power. This edge computing approach eliminates the need to downlink massive raw datasets, instead transmitting only the processed 3D models and analysis results.
“We’re essentially running a miniature supercomputer in orbit,” explains Dr. Sarah Chen, CTO of OrbitalMind, one of the companies behind the technology. “The AI can make decisions about what to image, when to switch sensors, and how to optimize data collection—all autonomously.”
Industry Implications: A New Space Race
Commercial Applications
While military surveillance grabs headlines, the commercial applications are equally transformative:
- Urban Planning: Cities can create up-to-date 3D models for infrastructure development
- Disaster Response: Rapid damage assessment after natural disasters
- Agriculture: Precision farming with real-time topographical analysis
- Mining: Exploration and volume calculations for resource extraction
- Insurance: Property assessment and risk modeling
Geopolitical Ramifications
The democratization of advanced surveillance capabilities through commercial providers is reshaping global power dynamics. Nations without traditional spy satellite networks can now purchase near-real-time intelligence from private companies, potentially destabilizing existing security arrangements.
Dr. Michael Torres, a space policy expert at Georgetown University, warns: “We’re entering an era where a startup with a few hundred million dollars can achieve surveillance capabilities that once required superpower budgets. This levels the playing field in ways we’re only beginning to understand.”
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Data Processing Bottlenecks
The sheer volume of data generated by modern Earth observation satellites—terabytes per second—has historically been a major bottleneck. The new AI system addresses this through:
- Intelligent data compression algorithms that preserve critical features
- Selective downlinking based on AI-determined importance
- Onboard feature extraction to reduce bandwidth requirements by 95%
Atmospheric Interference
Weather conditions and atmospheric distortion have long plagued satellite imaging. The AI system employs generative adversarial networks (GANs) trained to “see through” clouds and correct for atmospheric effects, achieving clear imaging even in challenging conditions.
Future Possibilities: What’s Next?
Swarm Intelligence
Companies are already developing constellations of AI-powered microsatellites that can coordinate autonomously. These swarms will enable:
- Continuous global monitoring with no gaps
- Adaptive targeting based on detected anomalies
- Collective decision-making about resource allocation
- Redundant coverage resistant to anti-satellite measures
Predictive Analytics
Future iterations will incorporate predictive capabilities, analyzing patterns to forecast:
- Military base expansion plans
- Supply chain disruptions
- Environmental changes
- Infrastructure development trends
Integration with Other AI Systems
The real power emerges when satellite AI integrates with other systems:
Example Scenario: A satellite detects unusual construction activity at a port facility. The AI automatically tasks nearby satellites for closer inspection, cross-references shipping data to identify associated vessels, analyzes supply chain databases to determine cargo origins, and generates a comprehensive intelligence report—all within hours.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Implications
The technology raises profound questions about privacy in an age of ubiquitous surveillance. While military bases are legitimate intelligence targets, the same capabilities could monitor private citizens, commercial facilities, or sensitive locations.
Current regulations, designed for an era of government-controlled satellites, struggle to address commercial capabilities. The Outer Space Treaty and related agreements say nothing about private AI-powered surveillance, creating a legal vacuum that companies are racing to fill.
The Road Ahead
As AI satellite technology continues advancing, we can expect:
- Resolution improvements enabling identification of individual objects
- Real-time video streaming from orbit
- Hyperspectral analysis revealing chemical compositions
- Quantum-enhanced sensors for unprecedented sensitivity
The single-pass 3D mapping of the Chinese naval base represents more than a technical achievement—it’s a harbinger of a world where no activity can escape detection, where privacy becomes increasingly precious, and where the balance of power shifts toward those who control information.
For businesses, governments, and individuals alike, adapting to this new reality will require not just technological solutions, but new frameworks for governance, ethics, and international cooperation. The AI satellites are watching, and they’re getting smarter every day.