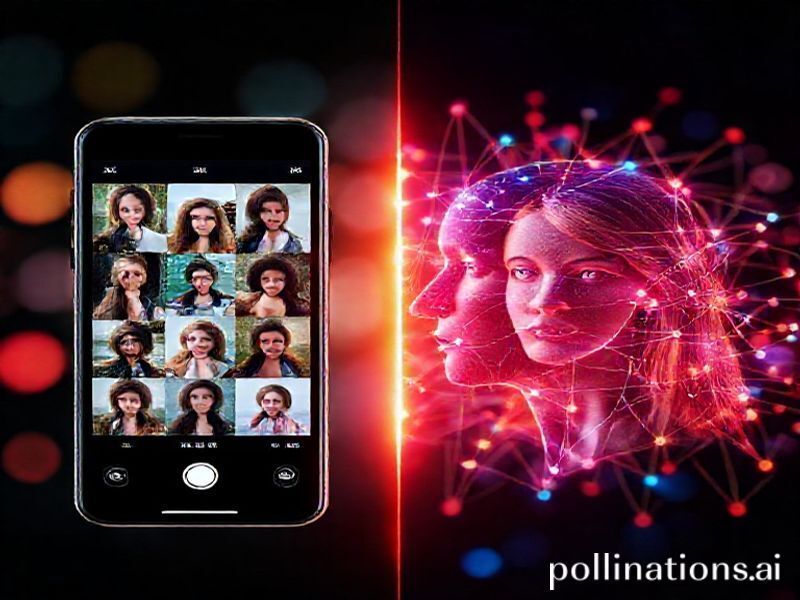
Tinder’s Chemistry AI: The $14 Million Gamble on Camera Roll Mining
In a bold move that’s sending shockwaves through both the dating and AI industries, Tinder has unveiled “Chemistry AI” – a controversial new feature that analyzes users’ camera rolls to boost match compatibility. Despite facing potential regulatory fines of up to $14 million under GDPR and similar privacy laws, the Match Group-owned platform is betting big on computer vision and machine learning to revolutionize how we find love online.
The Technology Behind the Controversy
Chemistry AI represents a quantum leap in dating app sophistication. Unlike traditional algorithms that rely on explicitly provided preferences and swipe patterns, this system delves into the visual diary of users’ lives. By analyzing thousands of personal photos, the AI constructs a nuanced profile of interests, lifestyle patterns, and personality traits that users might not even consciously recognize about themselves.
How It Works
The system employs a sophisticated multi-modal AI architecture that combines:
- Computer Vision Models: Trained on millions of images to identify objects, activities, locations, and social contexts
- Behavioral Pattern Recognition: Analyzes photo-taking frequency, timing, and composition preferences
- Social Graph Analysis: Identifies relationship patterns through group photos and recurring faces
- Interest Inference Engine: Maps visual content to personality traits and lifestyle preferences
The AI doesn’t just catalog what’s in photos – it interprets the story they tell. A user with frequent hiking photos taken at dawn might be flagged as adventurous and disciplined, while someone whose camera roll features numerous close-up food shots might be categorized as cultured and social.
The Privacy Paradox
Despite requiring explicit opt-in consent, Chemistry AI has ignited a firestorm of privacy concerns. The feature requests access to users’ entire photo libraries, not just selected images they choose to share. This comprehensive data mining approach has drawn criticism from privacy advocates and regulatory bodies across multiple jurisdictions.
Regulatory Risks and Revenue Implications
The $14 million revenue risk stems from potential GDPR violations alone. European data protection authorities have already indicated that scraping camera rolls for dating purposes may violate several key principles:
- Purpose Limitation: Users grant photo access for profile creation, not comprehensive behavioral analysis
- Data Minimization: Collecting thousands of photos when dozens would suffice
- Informed Consent: Questions about whether users truly understand what they’re agreeing to
- Right to Explanation: The AI’s black-box nature makes it difficult to explain why specific matches are suggested
Beyond regulatory fines, Tinder faces potential class-action lawsuits and user exodus risks. Competitors like Bumble and Hinge are already capitalizing on the controversy by emphasizing their commitment to privacy-first approaches.
Industry Implications and Competitive Response
Chemistry AI’s launch has triggered an arms race in the dating app industry. Major players are scrambling to develop competing technologies while navigating the ethical minefield of personal data usage.
The New Competitive Landscape
Industry analysts predict several key developments:
- Privacy-First Innovation: Expect emergence of “ethical AI” dating apps that promise similar compatibility matching without invasive data collection
- Federated Learning Adoption: Companies may adopt privacy-preserving ML techniques that train on-device without uploading personal photos
- Transparency Tools: New features allowing users to see exactly what the AI learned about them and how it influences matching
- Subscription Tier Wars: Premium privacy features becoming a key differentiator
The controversy has also sparked renewed interest in decentralized dating platforms that use blockchain technology to give users complete control over their data.
Technical Innovation Beyond Dating
While the dating application grabs headlines, Chemistry AI’s underlying technology has far-reaching implications across industries:
Retail and E-commerce
Retailers are already exploring similar computer vision technology to analyze customers’ photo libraries for style preferences, enabling hyper-personalized shopping experiences. Imagine Amazon suggesting products based on the brands and styles appearing in your personal photos.
Healthcare and Wellness
Medical AI companies see potential in using photo analysis for early health interventions. Patterns in personal photos – from changes in skin tone to subtle weight fluctuations – could trigger preventive care recommendations.
Financial Services
Banks and insurers are investigating whether lifestyle indicators derived from photo analysis could improve risk assessment for loans and policies, raising both efficiency and ethical concerns.
Future Possibilities and Ethical Considerations
As we stand at this technological crossroads, several scenarios emerge for the evolution of personal AI analysis:
The Transparent AI Future
Regulatory pressure may force companies to develop “explainable AI” systems that provide clear insights into their decision-making processes. Users might gain access to dashboards showing exactly what their photos revealed about them, with the ability to correct or remove specific inferences.
The Consent Revolution
Forward-thinking companies might pioneer granular consent systems where users can selectively share different types of photo-derived insights. A user might allow analysis of their travel photos for matching with fellow adventurers while keeping their family photos private.
The Privacy-Preserving Alternative
Advances in homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation could enable AI analysis without exposing raw photo data. These cryptographic techniques would allow the AI to learn from photo patterns without actually “seeing” the images.
Practical Insights for Users and Developers
For users navigating this new landscape:
- Read the Fine Print: Understand exactly what data you’re sharing and how it will be used
- Audit Your Photos: Before granting access, review what personal information might be revealed
- Start Small: If trying Chemistry AI, begin with limited photo access before committing your entire library
- Monitor Your Matches: Pay attention to whether AI-suggested matches actually align with your preferences
For developers and entrepreneurs:
- Privacy by Design: Build privacy considerations into your AI systems from day one
- Transparency Tools: Develop user-friendly ways to explain AI decision-making
- Opt-Out Mechanisms: Ensure users can easily revoke access and delete their data
- Cross-Functional Teams: Include ethicists and privacy experts in AI development teams
Conclusion: Love in the Time of AI
Tinder’s Chemistry AI represents both the promise and peril of our AI-driven future. While the technology could genuinely help people find more compatible partners by understanding them better than they understand themselves, it also raises fundamental questions about privacy, consent, and the commodification of our most personal moments.
The $14 million revenue risk may seem substantial, but it pales compared to the potential market transformation at stake. As users increasingly prioritize meaningful connections over endless swiping, the dating apps that successfully balance AI sophistication with ethical data use will define the industry’s future.
Whether Chemistry AI becomes a cautionary tale or a pioneering success will depend largely on how Tinder navigates the coming months of regulatory scrutiny and user feedback. One thing is certain: the genie of personal AI analysis is out of the bottle, and its impact will extend far beyond the realm of dating apps into every aspect of our digital lives.